reading-mri-with-nibabel.md 3.5 KB
Reading Structural MRI with nibabel
This tutorial demonstrates how to read structural MRI data using
nibabel and nilearn in conjunction with almirah.
Setup
First, we'll import the necessary libraries.
import nibabel as nib
import nilearn as nil
from almirah import Layout
Loading the Data
Next, we'll set up the layout to access the structural MRI data.
lay = Layout(root="/path/to/data", specification_name="bids")
lay
This should output:
<Layout root: '/path/to/data'>
We can query the layout to find all anatomical files with the .nii.gz extension:
files = lay.query(datatype="anat", extension=".nii.gz")
Querying a Specific File
To query a specific file, we can filter by subject, datatype, suffix, and extension:
file = lay.query(subject="D0020", datatype="anat", suffix="T1w", extension=".nii.gz")[0]
print(file.rel_path)
This should output the relative path of the file:
sub-D0020/ses-101/anat/sub-D0020_ses-101_T1w.nii.gz
We can then download the MRI file:
file.download()
This confirms the download:
get(ok): sub-D0020/ses-101/anat/sub-D0020_ses-101_T1w.nii.gz (file) [from origin...]
Reading the MRI Data
Next, we read the MRI data using nibabel:
raw = nib.load(file.path)
type(raw)
This should output:
nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Image
We can inspect the header information of the MRI data:
print(raw.header)
This outputs the header information:
<class 'nibabel.nifti1.Nifti1Header'> object, endian='<'
sizeof_hdr : 348
data_type : b''
db_name : b''
extents : 0
session_error : 0
regular : b'r'
dim_info : 54
dim : [ 3 192 256 256 1 1 1 1]
intent_p1 : 0.0
intent_p2 : 0.0
intent_p3 : 0.0
intent_code : none
datatype : int16
bitpix : 16
slice_start : 0
pixdim : [1. 1. 1. 1. 0.0064721 0. 0.
0. ]
vox_offset : 0.0
scl_slope : nan
scl_inter : nan
slice_end : 0
slice_code : unknown
xyzt_units : 10
cal_max : 0.0
cal_min : 0.0
slice_duration : 0.0
toffset : 0.0
glmax : 0
glmin : 0
descrip : b'TE=2.9;Time=103137.087'
aux_file : b''
qform_code : scanner
sform_code : scanner
quatern_b : 0.0
quatern_c : -0.018800024
quatern_d : 0.0
qoffset_x : -95.44943
qoffset_y : -132.33757
qoffset_z : -134.27122
srow_x : [ 9.9929786e-01 0.0000000e+00 -3.7593402e-02 -9.5449432e+01]
srow_y : [ 0. 1. 0. -132.33757]
srow_z : [ 3.7593581e-02 0.0000000e+00 9.9929309e-01 -1.3427122e+02]
intent_name : b''
magic : b'n+1'
We can also get the raw data as a NumPy array:
raw_data = raw.get_fdata()
type(raw_data)
This should output:
numpy.ndarray
And we can check the shape of the raw data:
raw_data.shape
This gives the shape of the data:
(192, 256, 256)
Visualizing the MRI Data
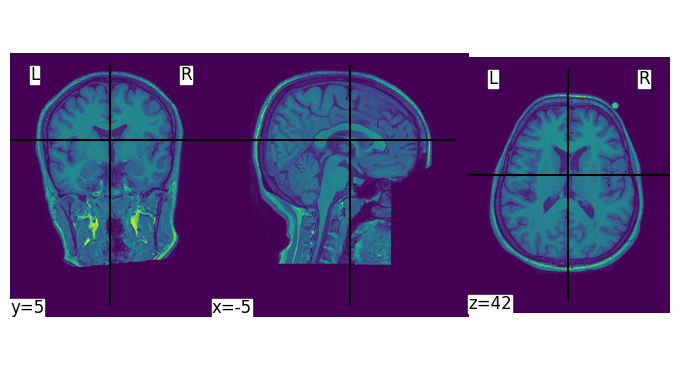
Finally, we use nilearn to plot the MRI data:
from nilearn import plotting
plotting.plot_img(raw)
This will generate the plot:
This concludes the tutorial. You've learned how to read MRI data using
nibabel and nilearn.