average-eeg-across-disorders.md 5.7 KB
Average EEG signal across various disorders
This tutorial demonstrates how to compute and visualize the average
EEG signal across various disorders using mne, pandas, and
seaborn in conjunction with almirah.
Setup
First, we'll import the necessary libraries and set the log level for MNE.
import mne
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from almirah import Dataset
mne.set_log_level(False)
Loading the Dataset
Next, we'll load the dataset and query the EEG files.
ds = Dataset(name="calm-brain")
eeg_header_files = ds.query(datatype="eeg", task="rest", extension=".vhdr")
eeg_data_files = ds.query(datatype="eeg", task="rest", extension=".eeg")
len(eeg_data_files)
This should give the total number of EEG files:
1120
We then download the EEG data files.
for file in eeg_data_files:
file.download()
Querying the Database
We connect to the database and query the presenting disorders table.
db = ds.components[2]
db.connect("username", "password")
df = ds.query(table="presenting_disorders")
df[["subject", "session", "addiction"]].head()
This displays the first few rows of the queried table in a DataFrame format.
| subject | session | addiction | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | D0019 | 101 | 0 |
| 1 | D0019 | 111 | 0 |
| 2 | D0020 | 101 | 0 |
| 3 | D0020 | 111 | <NA> |
| 4 | D0021 | 101 | 0 |
Processing the EEG Data
We define functions to compute the mean EEG signal and retrieve the disorders.
def get_eeg_mean(file):
raw = mne.io.read_raw_brainvision(file.path)
return raw.get_data().mean()
def get_disorders(file):
disorders = []
subject, session = file.tags["subject"], file.tags["session"]
filtered_df = df[(df["subject"] == subject) & (df["session"] == session)]
if filtered_df.empty:
print(subject, session)
return None
for column in ["addiction", "bipolar", "dementia", "ocd", "schizophrenia"]:
presence = filtered_df.iloc[0][column]
if not pd.isna(presence) and presence:
disorders.append(column)
return disorders if disorders else ["healthy"]
def file_func(file):
mean_eeg, disorders = get_eeg_mean(file), get_disorders(file)
if not disorders:
return pd.DataFrame()
mean_df = pd.DataFrame({"mean": [mean_eeg] * len(disorders), "disorder": disorders})
return mean_df.dropna()
We process the EEG header files to compute the mean EEG signal and retrieve the disorders.
mean_dfs = list(map(file_func, eeg_header_files))
mean_dfs = [df for df in mean_dfs if not df.empty]
mean_df = pd.concat(mean_dfs, sort=False)
mean_df.head()
This displays the first few rows of the combined DataFrame.
| mean | disorder | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | -0.008766 | healthy |
| 1 | 0.000457 | addiction |
| 2 | -0.006335 | healthy |
| 3 | -0.002764 | healthy |
| 4 | -0.008269 | ocd |
We compute the mean EEG signal for each disorder.
mean_df.groupby("disorder").mean()
This displays the mean EEG signal for each disorder.
| mean | |
|---|---|
| disorder | |
| addiction | 0.003414 |
| bipolar | 0.001613 |
| dementia | 0.010485 |
| healthy | 0.002449 |
| ocd | -0.000875 |
| schizophrenia | 0.005444 |
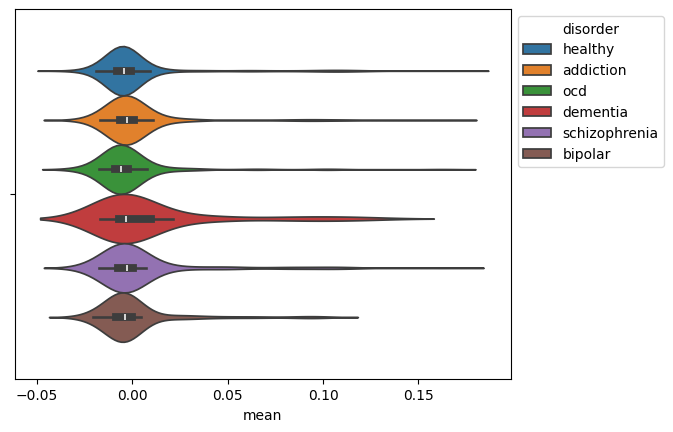
Visualizing the Results
We visualize the distribution of the mean EEG signal for each disorder using a violin plot.
ax = sns.violinplot(data=mean_df, x="mean", hue="disorder")
sns.move_legend(ax, "upper left", bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
This generates the plot:
This concludes the tutorial. You've learned how different modalities can be strung together to perform analysis involving multiple modalities.